Not an IASC member yet? Please follow this link to see membership options and benefits.
Abstract
Despite the effort to promote participative processes in the construction of policies, building functional polycentric and nested institutions remain a major challenge. Collaboration is fundamental to advance in the articulation of multi-scale instruments, the flow of information, grow of trust, and ultimately social learning, however, differences in the cognitive structures within groups of stakeholders is a major hurdle.
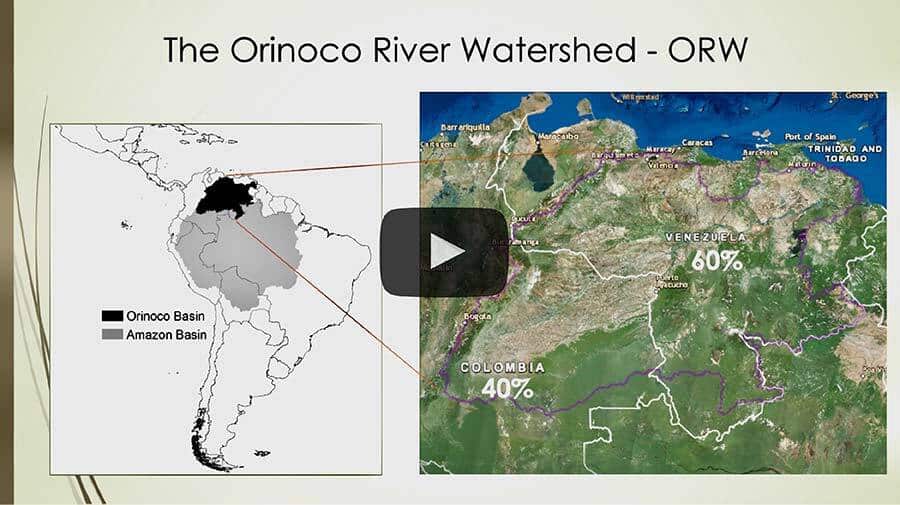
This research uses a survey to establish what cognitive variables impede collaboration between local and regional stakeholders in the Orinoco River Watershed, South America. This instrument captures information about the ideas and perceptions that four different groups of actors (Indigenous peoples, Non-Indigenous communities, Researchers, and Federal employees) have about use behavior, governance, and management of common-pool resources. Major cognitive differences between actors are tested using chi-square and the topologies of interaction are defined through social network analysis.
It was found that horizontal differences between groups of actors at the local scale are larger than at regional scales (40% and 10% respectively), also, Indigenous peoples have the largest cognitive differences. Despite this, all groups agree that larger opportunities for the protection of common-pool resources are found within Indigenous territories. The findings from this research indicate that indirect use of resources is a major obstacle impeding the interaction between local groups, this, together with differences in the perceptions about management practices, set Indigenous peoples completely isolated from the three remaining groups. Field observations and interviews revealed the material causes for such separation. The results from this research can help decision makers to identify and further exploring bridging opportunities and policies to improve conditions for better interaction between multi-scale actors.